Recommended LDL values corresponding to the risk level.
E. Gulbis Laboratorija has responded to the call of the Latvian Cardiology Society to introduce in all laboratories of Latvia common (uniform) reference values for four lipid fractions, to indicate LDL reference value corresponding to the cardiovascular risk level, as well as to indicate Ne-ABLH non-HDL indicators – as it is defined in the latest European Cardiology Association guidelines in 2012.
Ne-ABLH non-HDL (no high level density cholesterol)
It is calculated: KH-ABLH Total Cholesterol – HDL (common cholesterol – high density lipoprotein cholesterol).
This indicator shows not only ZBLH (LDL)(low density cholesterol), but also very low density lipoprotein cholesterols, which are the main triglyceride carriers.
Studies have proven that non-HDL ne-ABLH better than LDL ZBLH reflects the possibility of cardiovascular risk in cases when triglyceride level is increased.
Normative values are not presented.
LDL recommended values according to the cardiovascular risk level
| Patients with previously stated low or moderate risk | must be ˂ 3.0 mmol/L | Patients with previously stated high risk | must be ˂ 2.5 mmol/L | Patients with previously stated very high risk | must be ˂ 1.8 mmol/L |
A family doctor assesses the cardiovascular risk level for each patient individually.
In Latvia so-called SCORE (systematic coronary risk evaluation) system is used to evaluate cardiovascular disease risk.
In SCORE system risk is determined according 5 criteria:
- Gender
- Age
- Smoking
- Systolic blood pressure level
- Total cholesterol
However, it should be noted that these risk assessment principles refer to individuals who have not developed cardiovascular disease yet. It should be noted/stressed that patients with already diagnosed CV disease automatically are included into a high risk group and in this case there is no need for the risk calculation according to the SCORE system.
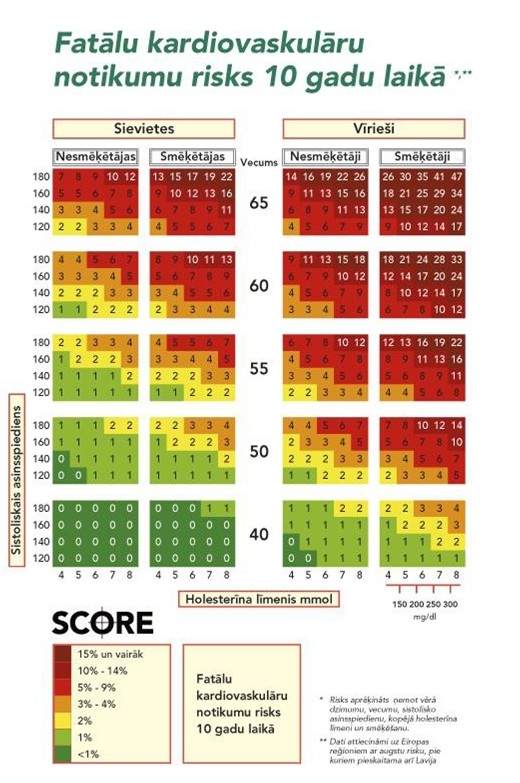
Risks of fatal cardiovascular events, taking into account KH correlation against ABLH Total Cholesterol and HDL ratio (after SCORE system)
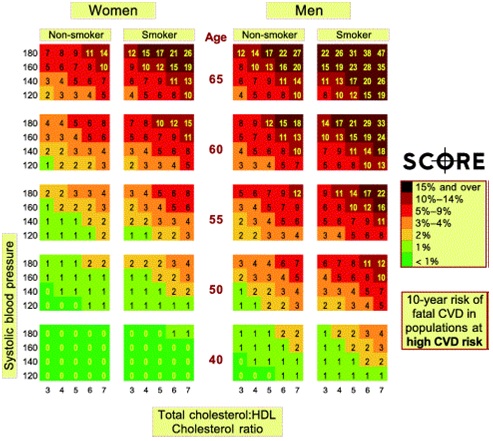
* Risk is calculated taking into account gender, age, systolic blood pressure level, total cholesterol level and smoking.
** Data are related to the European regions with high risk, Latvia is also included there.
Risk assessment steps:
- Does a patient have a cardiovascular disease (coronary heart disease), cardiovascular disease, peripheral artery disease) ?
According to the European CVD prevention guidelines all patients automatically are considered as high risk individuals. - Does a patient have:
- 2nd type sugar diabetes Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) or 1st type sugar diabetes Type 1 diabetets with microabuminuria or
- total cholesterol ≥8.0 mmol/L and /or ZBLH LDL≥ 6.0 mmol/L or
- a heavy arterial hypertension(AH ≥180/≥110 mmHg)
Any of the mentioned criteria classifies a patient as a high risk individual.
- The total fatal cardiovascular event absolute risk is calculated according to the SCORE system. If cardiovascular death risk in the nearest 10 years is ≥ 5%, a person is included in a high risk group.
- Does a patient have metabolic syndrome?
- If a person does not fit in any of the above mentioned categories, but the SCORE risk is moderate (3 – 4% in 10 years), then the absolute risk may by higher if there are separate additional risk factors:
- Early cardiovascular disease to the first-degree relatives;
- Pronounced abdominal obesity (waist for men ˃ 102 cm or women ˃ 88 cm);
- Body mass index ˃ 30 kg/m2;
- Low HDL level ABLH (for men ˂ 1.0 mmol/L or for women ˂ 1.2 mmol/L);
- High triglycerides level (˃ 1.7 mmol/L);
- Fasting hyperglycemia (˃ 6.1 mmd/L) or glucose tolerance disorders;
- Repeatedly elevated CRO CRP;
- Early menopause;
- Left ventricular hypertrophy.
Thought in such cases it is not possible precisely determine the risk, it can be assumed that each individual additional risk factor the absolute risk will increase the absolute risk not more than 1 %. If in this way adjusted risk reaches 5%, then the person is classified as high risk.
It is recommended to select a very high risk group of patients who need a maximum amount and intensity of preventive measures. Very high risk patients are:
- Patients with an acute coronary syndrome;
- Patients with a coronary heart disease and:
- multiple, poorly controlled, underlying risk factors, in particular diabetes mellitus, smoking;
- with certain specific risk factors (hipercholest hypercholesterolaemia ≥ 8.0 mmol/L, grade 3 arterial hypertension);
- metabolic syndrome.
- Patients with 2-pool KVS (coronary heart disease + cerebrovascular disease or peripheral arterial disease or other cases).